where, σ=normal stress, or tensile stress, pa
P=force applied, N
A=cross-sectional area of the bar, m2
=shearing stress, Pa
As=total area in shear, m2
where,
=tensile or compressive strain, m/m
=total elongation in a bar, m
=original length of the bar, m
Stress is proportional to strain
where,
E=proportionality constant called the elastic modulus or modulus of elasticity or Young’s modulus, Pa
where,
v=Poisson’s ratio
=lateral strain
=axial strain
where,
=change in volume
=original volume
=strain
=Poisson’s ratio
where,
=total elongation in a material which hangs vertically under its own weight
W=weight of the material
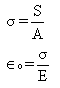
where,
=Circumferential or hoop Stress
S=Circumferential or hoop tension
A=Cross-sectional area
=Circumferential strain
E=Young’s modulus
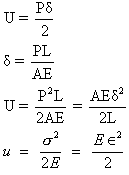
where,
U=total energy stored in the bar or strain energy
P=tensile load
=total elongation in the bar
L=original length of the bar
A=cross-sectional area of the bar
E=Young’s modulus
U=strain energy per unit volume

where,
=normal or circumferential or hoop stress in cylindrical vessel, Pa
=normal or circumferential or hoop stress in spherical vessel, Pa and longitudinal stress around the circumference
P=internal pressure of cylinder, Pa
r=internal radius, m
t=thickness of wall, m
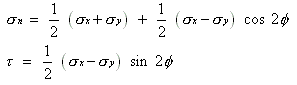
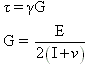
where,
=Shearing Stress, Pa
=Shearing Strain or angular deformation
G=Shear modulus, Pa
E=Young’s modulus, Pa
V=Poisson’s ratio
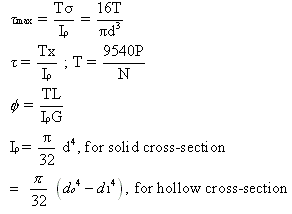
where,
=maximum shearing stress, Pa
r=radius of the section, m
d=diameter of a solid circular shaft, m
=polar moment of inertia of a cross-sectional area, m4
T=resisting torque, N-m
N= rpm of shaft
P=power, kW
L=length of shaft, m
G=shear modulus, Pa
do=outer diameter of hollow shaft, m
di=inner diameter of hollow shaft, m
and
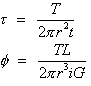
where,
=Ip, polar moment of inertia for thin-walled tubes
r=mean radius
t=wall thickness
Flexure Formula
where,
=Stress on any point of cross-section at distance y from the neutral axis
=stress at outer fibre of the beam
c=distance measured from the neutral axis to the most remote fibre of the beam
I=moment of inertia of the cross-sectional area about the centroidal axis
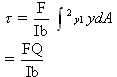
where,
F=Shear force
Q=statistical moment about the neutral axis of the cross-section
b=width
I=moment of inertia of the cross-sectional area about the Centroidal axis.
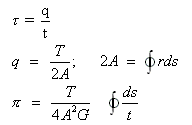
where, =shearing stress at any point of a blue
t=thickness of tube
q=shear flow
T=applied torque
R=distance between a reference point and segment ds
Π=angle of twist of a hollow tube

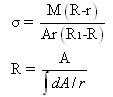
where, =normal stress
M=bending moment
dA=cross-sectional area of an element
r=distance of curved surface from the centre of curvature
A=cross-sectional area of beam
R=distance of neutral axis from the centre of curvature
R1=distance of centroidal axis from the centre of curvature
(a) Bending of a Beam Supported at Both Ends
(b) Bending of a Beam Fixed at one end
where, d= bending displacement, m
F=force applied, N
I=length of the beam, m
a=width of beam, m
b=thickness of beam, m
Y=Young’s modulus, N/m2
Walang komento:
Mag-post ng isang Komento